The evolution of SOC has evolved with security threats and business changes. So far, SOC has developed three generations, from the asset-based 1.0, the business-based 2.0, to 3.0 with comprehensive threat perception and response. This article will take you to review the past and present of the SOC and explore the future development.
Security Operations Center 1.0 - from the perspective of asset
In the early stage of information security construction, security equipment and systems were deployed, which gradually becomes defense silo leading to huge management cost but low efficiency. For this reason, the earliest security management system appears. Realize the centralized monitoring and policy dispatch of firewall/VPN to build perimeter security protection system.
With the deeper understanding of information security, the idea of security management systemization has gradually matured. A comprehensive security monitoring, analysis and response system with information system assets-centric, Security Operation Center 1.0 has emerged. It takes assets as the mainline and performs incident management and treatment process, as well as a risk management and operation process.
1. Assets as the Mainline
2. Incident Collection and Management
3. Service Content: Risk Management and Security Operation and Maintenance.
With the deepening of customer business and industry demands, the limitations of the traditional SOC 1.0 concept and technology have gradually appeared, which are mainly reflected in three aspects:
1. In system design, asset-oriented and lack business analysis.
2. In technical support, short of business security information collection.
3. In implementation process, fail in customer business driven.
With assets as the core and lack of business perspective, traditional SOC cannot truly meet the requirements of customers.
Security Operations Center 2.0 - from the perspective of business
The emergence of SOC 1.0 improved the level of user information security management, and thus has higher expectations. For users, security is not simply equipment security but business security. The security management of IT resources is not the goal. The core requirement is to ensure the availability, continuity, and security of the business carried by IT resources. Because business is the lifeline of enterprises and organizations. It is required to establish a business-centric management system for users to ensure business security. Inspect operation and security of IT resources from a business perspective. Thus, the business-oriented SOC 2.0 appears.
The SOC 2.0 inherits and develops the centralized management concept of the SOC 1.0, incorporates with security and business, and truly builds an integrated security system from the perspective of customer business value.
Definition of SOC 2.0: an integrated security management system with business as the core. Start from the business and adopt business demand analysis, business modeling, business-oriented security domain and asset management, business continuity monitoring, business value analysis, business risk and impact analysis, business visualization and other links. Use the proactive and reactive combination method collects security information from various IT resources. Normalize, monitor, analyze, audit, alert, respond, store and report from a business perspective. The SOC 2.0 takes business as the core and runs through the various stages of the information security management system life cycle construction from research, deployment, implementation to operation and maintenance.
The value of SOC 2.0 is to ensure that IT is reliable and securely consistent with the customer’s business strategy, prompting customers to effectively use information resources and reducing operational risks.
From the SOC 1.0 to the SOC 2.0, the integration of business and security has been achieved from product aspects.
From a service perspective, the SOC will become the service support platform of MSSP (Managed Security Service Provider), the technical support platform of SaaS (software as a service, security as a service), and the security management backend of cloud computing and cloud security. All security services sensed by users will be supported by the SOC. On the one hand, the business concepts and ideas of the SOC products will inject into the SOC services; on the other hand, the improvement of the SOC service level and customer awareness will also promote the development and maturity of the SOC products.
The SOC 2.0 also initially defines the security management process, which corresponds to the three stages of security incident management. Deployment of protective measures is the key point in beforehand stage. Security monitoring and emergency response during the incident. Post-analysis and investigation of events that are not alerted in the monitoring after the incident.
Security Protection Management: responsible for the management of security equipment and the operation of the basic security system. It is a variety of protection management before the emergence of a security incident. Its distinctive feature is to generate and distribute security policy to related security equipment.
Monitoring and Emergency Dispatch Center: comprehensive analysis of security incidents, prewarnings based on the degree of threat, and timely response to incident.
Audit Management Platform: forensics and reproduction of incidents, security compliance audit, statistical analysis, and historical data mining. Security audit is the "summary" of security management, which is also the basis for security protection.
Security services run through three dimensions. The protection policy requires an overall assessment of security. The prewarning emergency requires the analysis and methods of security experts... The functional requirements of the three development directions of the SOC can be independent but have same source, from security log and link data analysis. The construction of SOC is like three flowers blooming on a root.
The key to security management is to consider comprehensively, and omission will bring insecure factors to the system. Therefore, the three dimensions of the SOC should be mutually complementary. No single aspect can replace the functions of other aspects. Combining these aspects to cover the entire cycle of a security incident can secure the customer business.
Security Operations Center 3.0 - from the perspective of city-level operations with comprehensive threat perception and response
Although the SOC 2.0 considers the customer’s business and addresses security threats and risks based on the business. APT attacks such as Google Aurora attack, Stuxnet attack, and night dragon attacks have reflected new attack methods and methods of attack are changing since 2010. Zero-day vulnerability attacks, spear phishing attacks, using vulnerabilities to gain initial control remotely. Watering hole attacks, ransomware, APT attacks, and professional attack organizations have formed the protagonists of the latest attacks. The emergence of these new attack methods and attackers has completely broken the traditional passive defense system.
There are always people who better than you. Information security is the confrontation between offense and defense, achieving a dynamic balance in a process. The passive protection cannot defend long-planned attacks. Any defense based on ‘rule’ cannot avoid being deceived or bypassed. Therefore, the adaptive security architecture proposed by Gartner emphasizes the importance of detection, prewarning, and response. Gartner predicts that by 2020, preventive measures will no longer be important. The key is monitoring and intelligence. 60% of the security budget will be invested in detection and response.
How to achieve information security and respond to the increasing security threats? At present, both users and security practitioners have shifted from protection only to prewarning, detection, and response. Security capabilities have shifted from prevention to rapid detection and response. Real-time defense will be based on "Intelligence-centric", it no longer emphasizes single point detection, and no longer purely pursues the accuracy of alerts, but connects several points and uses data as the driven to solve problems.
The best way to solve this problem is to establish a managed third-party SOC based on cloud computing and big data analysis from vendor and customer perspectives. It can settle network security provisioning on the government and enterprise sides.
Establish a third-party independent SOC. Provide managed and outsourcing 7*24 professional security operation services for government agencies, enterprises, and smart city. Create full-time cybersecurity emergency response center to improve the detection and response capabilities of government agencies, enterprises and strengthen the monitoring and investigation capabilities of potential attack. Regional third-party SOC provide professional managed security services for cities, which is a effectively way to improve the network security capability of city. It is the best choice for solving the "last mile" of security capability delivery. In recent years, it has gradually become an important direction for the development of domestic and international network security industries.
The SOC 3.0 will focus on the following four aspects of the third-party security operation center:
Comprehensive Perception Basic Capacity Building
The comprehensive refers to the ability to perceive intelligence related to information security. Comprehensive security monitoring is the basis of the security technical means of the security operation platform. Data collection and analysis of endpoint, cloud, and data channel form whole security posture as basic data services. Including: equipment operating status, assets, websites, endpoint events, security logs, traffic, threats, vulnerabilities, tactics and techniques, security status and security capabilities perception.
Currently, the alert and response capabilities acquired by users come from the threats and vulnerability analysis reports of security equipment. But lack of self-security status inspection. For example: the security status of critical business systems and important data, the implementation of security protection capabilities, and the perception of violations of internal threats.
Secondly, the methods and tactics of threat actor cannot be discovered or understood or updated in time. The existing security technology and management are not targeted which lead to information security system failure.
In this regard, the ATT&CK knowledge base released by MITER is an effective way to understand what tactics and techniques are used by attackers to compromise enterprise information systems.
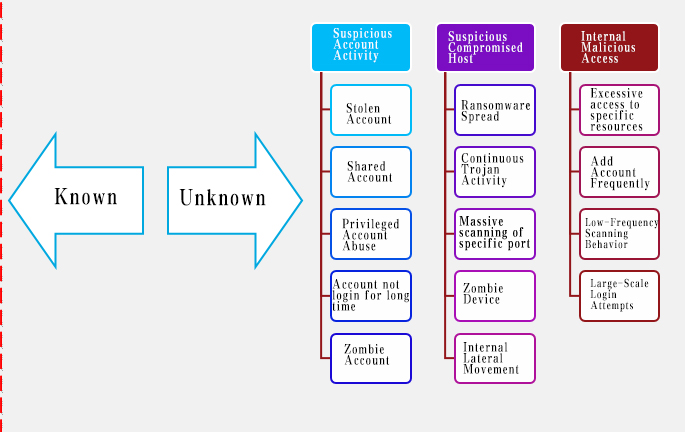
Build Clue Discovery for Abnormal Behavior
Traditional threat monitoring based on correlation rules cannot detect advanced persistent threats. Because the timeline of APT attacks may continue several years with multiple action and movement. However, from the beginning to the end of the attack, the entire attack process will continue multiple "action". Each action must be different from normal user behavior, such as: search important asset information, access to many systems and data, unauthorized access to sensitive data, acquire critical business systems and data, hide crumbs and operations, login different devices with the same identity, etc. For attackers who have penetrated the system, abnormal behavior detection becomes the only opportunity to identify this type of threat. Therefore, the detection and prewarning of abnormal behaviors of users and devices within an enterprise is the key to discovering advanced security threats.
Build the enterprise information security intelligence system using various data sources to perceive Who, When, Where, How, What, and profile user and device. It’s the basis for discovering abnormal behaviors, whether it is through automatic machine learning or manual analysis.
On this basis, based on UEBA technology, through the analysis and mining of abnormal behaviors that deviate from the "normal" mode, detect threatening users and entities. Use machine learning, algorithms, and statistical analysis to understand when the deviation has been established. By comparing with the original behavior model, and analyzing the abnormal behavior models of other dimensions, find out which accounts may be stolen and controlled. Uncover abnormal type, details, and traces to display which abnormalities may lead to potential real threats. It is a powerful tool for detecting abnormal behaviors of internal users and identifying threats. Aggregate data in reports and logs, file, flow, and packet to reduce noise of massive data, decrease workload of security event analysis, improves the pertinence and accuracy of alerts. Find more values combining with SIEM and other security management platforms.
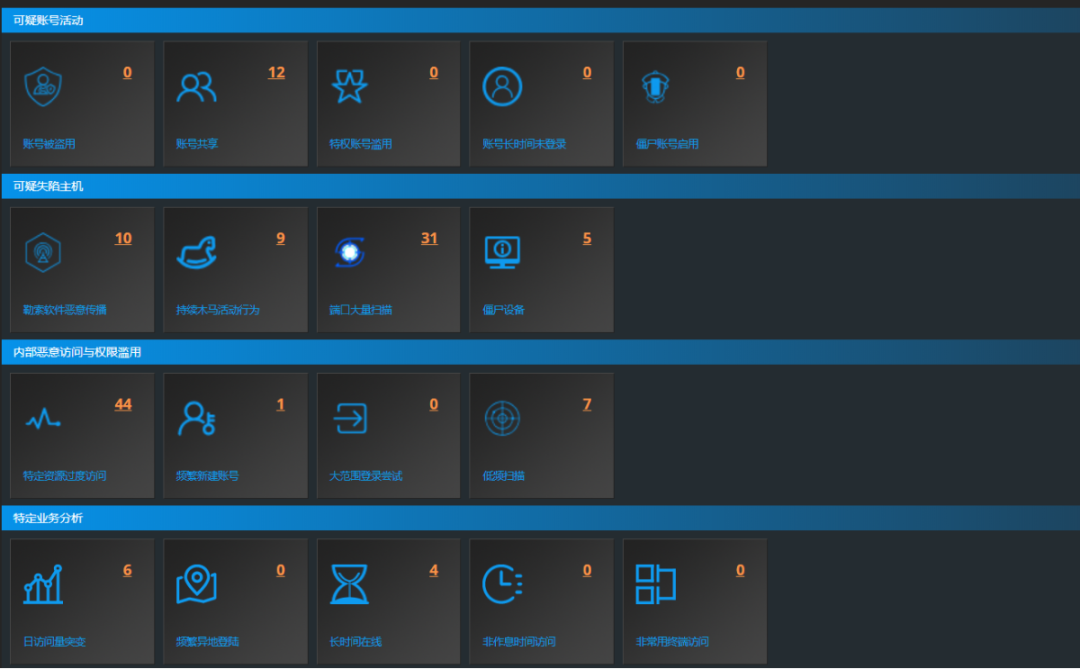
Build Critical Event Analysis Capability
Abnormal behavior is an important clue to a security incident. Tier1 security analyst is hard to identify and trace clue due to limit of trustable raw data, in a passive defense situation. It is crucial to construct the drilling, correlation, and mining of abnormal behaviors, which can turn passive defense into active defense. Connect a series of clues. The truth is approached by points and faces. For example: from suspicious IP to access user, from suspicious user to application, database or sensitive file, the behavior sequence of malicious behaviors can be determined in the time dimension. And further locate the threat. Perform investigate and forensics for attack IP and attacked IP through original traffic packet of the attack or internal abnormal behavior to confirm whether it has penetrated the intranet.
Quantify the attacker's destructiveness (attack force value) and attack intensity (attack value) through machine learning algorithms, and automatically block high-risk IP address.
Compare with internal threat intelligence database, automatically/manually block IP address (security device telemetry).
The above process must rely on a professional data analysis platform which can aggregate data sources, draw a portrait of enterprise information system through data mining, profile characteristics of user and device, automatically detect and prewarn abnormal behaviors, correlate user, equipment, application, and data in time series with clues of abnormal behavior, integrate with threat intelligence to set threat indicators, and combine professional security analysts to finally locate threats.
Build Security Closed-Loop for Timely Response
Security starts with "detection" and ends with "response". Before the attacker causes damage to the enterprise information system, stopping the damage or reducing the loss is the ultimate defense line of information security system. And it is also the goal of timely response. When a threat is detected, the timely response depends on the security ecology. Now the work intensity and pressure of security personnel are extremely high. Products that can reduce workload and improve efficiency will certainly be popular, such as SOAR (Security Orchestration Automation and Response). Different systems or different components within a single system can be combined according to a certain logical relationship through API (Application Programming Interface) and manual checkpoints. It completes the process of a specific security operation and enables integration with multi-service systems, multiple devices, and multi-level according to predefined logic when an alert is triggered, realizing semi-automatic security incident response.
Outlook
In the future, an important task of the security operation center is to combine the actual combat scenarios of personalized security operation centers across the country, aggregate and output different security capabilities, and deeply integrate artificial intelligence technology, continuously improve the management level of security operations, and standardize the output of operation scripts, ATT&CK attack models, and threat intelligence through industry standards. Accurately locate security incidents and improve the speed of response.
The working environment of security attackers will change from reactive combat to active combat
In the past, the research of security vendors was to passively deal with security problems in actual combat. Customers can only seek for help when find problems. The provincial and municipal SOC will build actual combat attack scenarios based on different businesses when vendor setup head SOC. In the future, the security offensive and defense research will belong to security operation center and conduct actual combat analysis to find high-risk security threats, APT attacks, and output ATT&CK attack models and security intelligence.
Personalized security operation center generated around business
According to the different business needs of customers, personalized security operation centers will be produced. Based on onsite heavyweight security operation services, a personalized security operation center will be built, which is oriented to customer needs and customized based on user status and security goals. Provide professional security service solutions and best practice services covering the entire life cycle of customer information system plan, design, implementation, operation, and continuous improvement.
Onsite heavyweight security operation services cover five categories: comprehensive security supervision services, comprehensive security operation services, data security special operation services, industrial control security special operation services, cloud security special operation services, and sub-catalogs. Provide users with a full range of security services and the entire process of worry-free security operation delivery.
The three-level security operation center will aggregate and output different security capabilities
The SOC can be divided into three-level in accordance with the scale of prefecture-level/industry-level security operation center, provincial-level security operation center, and manufacturer-level security operation center.
The prefecture-level/industry-level SOC will output realistic security scenarios, the provincial-level SOC will output experienced security analysts, and the manufacturer-level SOC will output discovery and operation capability in APT discovery, ATT&CK attack models, high-risk vulnerabilities, and security operation work scripts.
The prefecture-level/industry-level SOC fully build visual network situation awareness capabilities, and use different logical spaces to discover cybersecurity events, event impacts, and related actions. Create actual combat security offensive and defense scenarios, grasp the threat situation in time, and then make faster and smarter action decisions, and provide actual combat security scenarios for upstream SOC. The prefecture-level/industry-level SOC will build three capabilities:
1. Discover threat
2. Discover attack scenarios
3. Perceive offensive and defensive situation
The provincial-level SOC outputs experienced security analysts. Due to the lack of professional security operation talents and security analysts in the prefecture-level SOC, the provincial-level SOC will serve as a security operation resource pool which serve for security operation talents, such as security operations personnel, tier1 analyst, tier2 analyst. In addition, different SOC outputs different security operations talents, such as: data security, cloud security, OT/IoT security.
The manufacturer head SOC, as the main technical capability output resource pool, actively builds the security operation center management resource pool, the security tool development capability resource pool, combining the actual offense and defense scenarios provided by the prefecture-level and provincial-level SOC, connecting tier3 security analysts, continues to output APT discovery, ATT&CK attack model, high-risk vulnerability, security operation work script and other attack discovery capabilities and operational capabilities, and threat perception capabilities and security operation management for prefecture-level and provincial-level SOC.
The Birth of Internal Threat Intelligence
The personalized security operation center must derive internal threat intelligence that suits operation center business.
Currently, public threat intelligence, a security data source, becomes a problem for security teams:
Numerous, data sources and quantity, plus confidence will cause many false positives alerts leading to swamp.
Complex, the type, application scenarios. Different intelligence may be located at different stages of the attack chain. Different scenarios focus on different attackers. For example, the intelligence of the cloud platform focuses on external attackers. The intelligence on the enterprise side is mainly pay attention to identify whether there are infected hosts or malicious external behaviors in the intranet. The different types of threat intelligence used in different scenarios.
Fast, updated quickly. With the background of the "numerous" and "complex", the update speed may become the last straw that overwhelms security managers. If there is no suitable intelligence automation operation process, this series of intelligence detection, event tracking, event confirmation and threat tracing will be a work in an extremely low human input-output ratio.
Therefore, it is crucial to build the internal threat intelligence, which is based on the personalized security operation center’s attack scenarios to conduct actual combat analysis, determine attack action, attack technique, attack tool, and exposed vulnerability, especially in different business areas, such as big data, data security, and cloud security. The attack action, technique, vulnerability, and tool are different. Create internal threat intelligence will quickly locate the attack process of security incidents for different personalized security operation centers, respond to the impact of attack events, and actively provide recommendations. This is also a quantifiable indicator for measuring the capabilities of security operations centers in the future.
Have a question? We're here to help.
Please send an email to overseas@venustech.com.cn
Or you can fill out the form below and we will get in touch with you soon.
Thank you for your interest in Venustech.